给你一座由 n x n 个街区组成的城市,每个街区都包含一座立方体建筑。给你一个下标从 0 开始的 n x n 整数矩阵 grid ,其中 grid[r][c] 表示坐落于 r 行 c 列的建筑物的 高度 。
城市的 天际线 是从远处观察城市时,所有建筑物形成的外部轮廓。从东、南、西、北四个主要方向观测到的 天际线 可能不同。
我们被允许为 任意数量的建筑物 的高度增加 任意增量(不同建筑物的增量可能不同) 。 高度为 0 的建筑物的高度也可以增加。然而,增加的建筑物高度 不能影响 从任何主要方向观察城市得到的 天际线 。
在 不改变 从任何主要方向观测到的城市 天际线 的前提下,返回建筑物可以增加的 最大高度增量总和 。
示例 1:
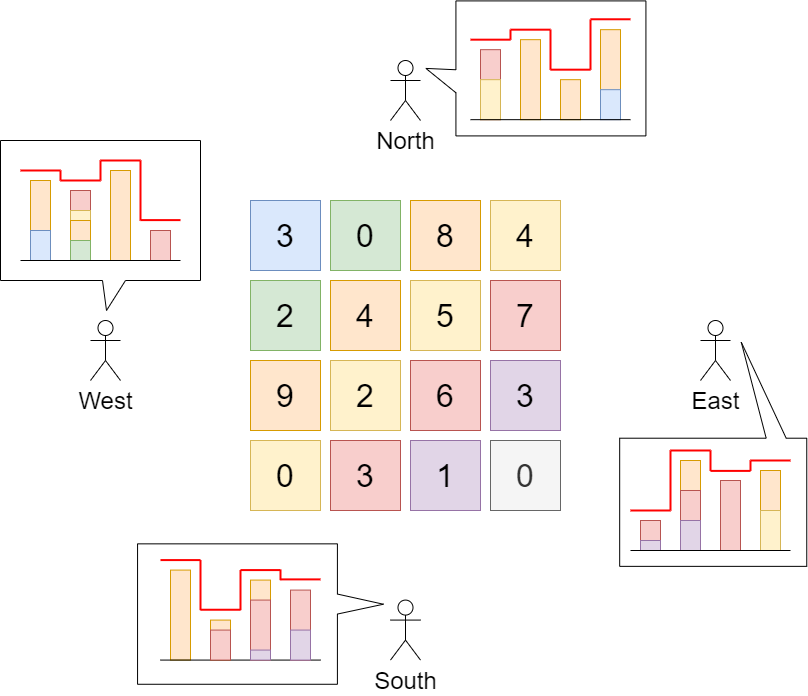
输入:grid = [[3,0,8,4],[2,4,5,7],[9,2,6,3],[0,3,1,0]]
输出:35
解释:建筑物的高度如上图中心所示。
用红色绘制从不同方向观看得到的天际线。
在不影响天际线的情况下,增加建筑物的高度:
gridNew = [ [8, 4, 8, 7],
[7, 4, 7, 7],
[9, 4, 8, 7],
[3, 3, 3, 3] ]
示例 2:
输入:grid = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]
输出:0
解释:增加任何建筑物的高度都会导致天际线的变化。
提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[r].length2 <= n <= 500 <= grid[r][c] <= 100
Related Topics